BaF2 Window
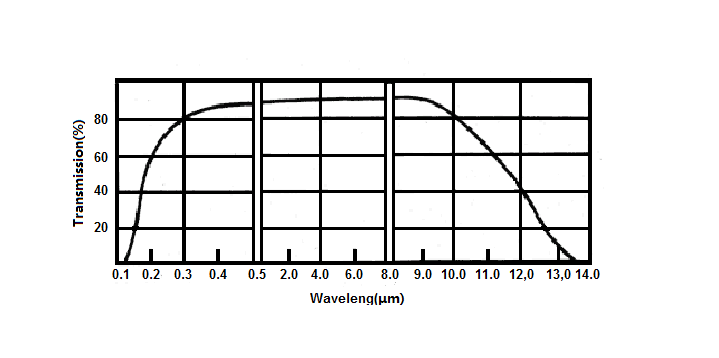
Barium Fluoride (BaF2) Windows can be used in a variety of applications, such as infrared spectroscopy, due to their wide broadband transmission that extends from the deep ultraviolet to the long-wave infrared. Barium fluoride’s low index of refraction of 1.48 provides high transmission without the need for anti-reflection coatings. Barium fluoride windows can be used up to 800°C in a dry environment, but prolonged exposure to moisture can degrade transmission in the vacuum ultraviolet range. While barium fluoride windows are less resistant to water than calcium fluoride, BaF2 windows are the most resistant optical fluoride to high-energy radiation, but feature lower UV transmittance. BaF2 has a Knoop hardness of 82.
Advantages
1 ) Excellent Transmission from 200nm – 12μm
2 ) Resistant to High-Energy Radiation
3 ) Provide High Transmission without AR Coatings
Specifications
1 ) Diameter: 3~200mm
2 ) Diameter Tolerance: +/-0.2mm
3 ) Thickness Tolerance: +/-0.03mm
4 ) Aperture: >90%
5 ) Surface Quality: 80/50~10/5 (S/D)
6 ) Parallelism: <1 arc minute
7 ) Chamfer: 0.3-0.5mmx45°
Optical Properties
Transmission Range | 0.15 to 12 micron |
Refractive Index | 1.45 at 5 micron |
Refractive Loss | 6.5% at 5 micron |
Crystal/Class Structure | Cubic CaF2 |
Cleavage Plane | (111), Perfect |
Thermal Properties
Thermal Expansion | 18.1×10-6/℃ at 273K |
Thermal Conductivity | 11.72 W m-1K-1 at 286K |
Melting Point | 1386 ℃ |
Specific Heat Capacity | 410 J Kg-1K-1 |
Mechanical Properties
Density | 4.89 g/cc |
Hardness(Knoop) | Knoop 82 with 500g indenter |
Youngs Modulus | 53.07 GPa |
Shear Modulus | 25.4 GPa |
Bulk Modulus | 56.4 GPa |
Poisson Ratio | 0.343 |
Elastic Limit | 26.9 Mpa (300psi) |
Molecular Weight | 175.36 |
Chemical Properties
Solubility | 0.17g/100g water at 23℃ |
Technical Images